Attached Pdf ES E247-A Braemar Residential Service Guide
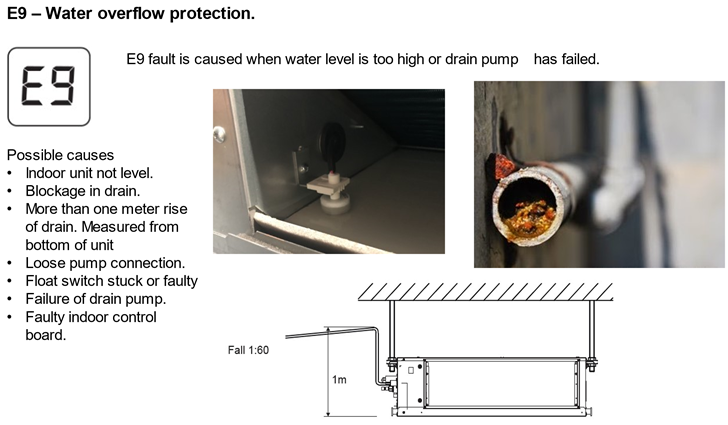
E9 Fault Diagnosis and Resolution
Issue:
The E9 fault means the indoor unit thinks condensation water isn't being pumped or drained properly.
Steps to Diagnose and Fix:
Check the Reservoir/Tank for Water:
- If there is water (Gravity Drain):
- Look for any blockages in the drain. If you find one, clear it, reset the power to clear the E9 fault, and turn the system back on.
- If there is no water:
- If resetting the power doesn't clear the fault, check the Float Switch:
- Make sure it's not stuck and is sitting correctly on its bracket.
- Check the plug connection on the Indoor PCB to ensure it's secure.
- Test the float valve plug for continuity.
- If it's an open circuit, replace the Float Switch.
- If it's not an open circuit, and the fault persists, replace the Indoor PCB.
- If resetting the power doesn't clear the fault, check the Float Switch:
- If there is water (Gravity Drain):
If there is water (Pump Drain):
- Manually drain the water, reset the power, and switch to cooling mode to see if the pump is working. (The pump runs in Cooling and Dry modes and continues for 2 minutes after the compressor stops to ensure all water is pumped away.)
- If the pump isn't working:
- Check the pump plug connection on the Indoor PCB.
- Test the power supply on the pump terminals while in cooling mode. It should be 240V.
- If there's voltage, replace the pump.
- If there's no voltage and the system is still calling for cooling, replace the Indoor PCB.
- If the pump isn't working:
- Manually drain the water, reset the power, and switch to cooling mode to see if the pump is working. (The pump runs in Cooling and Dry modes and continues for 2 minutes after the compressor stops to ensure all water is pumped away.)
FAQs
Q: What does the E9 fault mean?
A: The E9 fault indicates that the indoor unit suspects condensation water isn't being pumped or drained properly.
Troubleshooting Tip:
- Ensure the reservoir/tank is checked for water and follow the diagnostic steps to identify and resolve the issue.
Q: How do I clear the E9 fault?
A: Follow the diagnostic steps to check for blockages, ensure the Float Switch is functioning, and verify the pump operation. Reset the power after addressing any issues.
Troubleshooting Tip:
- After each step, reset the power to see if the fault clears. If not, proceed to the next step.
Q: What should I do if the Float Switch is stuck?
A: Ensure the Float Switch is not stuck in the up position and is correctly seated on its bracket. Check the plug connection and test for continuity. Replace the Float Switch if necessary.
Troubleshooting Tip:
- Gently move the Float Switch to ensure it isn't stuck. If it is, clean any debris that might be causing the issue.
Q: How do I check if the pump is working?
A: Switch the system to cooling mode and observe if the pump operates. If it doesn't, check the plug connection and power supply on the pump terminals. Replace the pump if voltage is present, or replace the Indoor PCB if no voltage is detected.
Troubleshooting Tip:
- Listen for the pump running in cooling mode. If silent, check connections and voltage as described.
Q: What if there's no water in the reservoir/tank?
A: If there's no water and the E9 fault persists after resetting the power, check the Float Switch and its connections. Replace the Float Switch or Indoor PCB as needed.
Troubleshooting Tip:
- Ensure the system is in a mode that generates condensation (Cooling or Dry) to verify if water should be present.
Glossary
- E9 Fault: An error code indicating an issue with condensation water not being pumped or drained properly.
- Reservoir/Tank: The container where condensation water collects.
- Gravity Drain: A drainage method relying on gravity to remove water.
- Pump Drain: A drainage method using a pump to remove water.
- Float Switch: A device that detects the water level in the reservoir/tank and signals the system accordingly.
- Indoor PCB (Printed Circuit Board): The main control board inside the indoor unit that manages various functions and connections.
- Continuity: A test to check if an electrical circuit is complete and unbroken.
- Open Circuit: A break in an electrical circuit preventing current from flowing.
